DIY hen house design offers a rewarding experience for chicken enthusiasts, allowing you to create a custom home for your feathered friends. Building your own hen house gives you complete control over the design, materials, and features, ensuring a safe and comfortable environment for your flock.
From choosing the right location and materials to planning the layout and construction, this comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of the process. Whether you’re a seasoned DIYer or a novice builder, this guide provides clear instructions and helpful tips to make building your own hen house a successful and enjoyable endeavor.
Introduction to DIY Hen House Design
Building your own hen house can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to create a custom space for your feathered friends while saving money compared to purchasing a pre-made coop. A DIY hen house provides flexibility in design, ensuring it meets your specific needs and preferences.
Choosing the Right Location and Materials, Diy hen house design
The location and materials used for your hen house are crucial for its functionality and longevity.
Location Considerations
- Sunlight: Hens need ample sunlight for vitamin D production and overall health. Choose a location that receives at least six hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Drainage: Ensure the location has good drainage to prevent water accumulation, which can lead to dampness and disease.
- Protection from Predators: Select a location that offers protection from predators like foxes, raccoons, and hawks. Fences, secure enclosures, and strategic placement can help deter predators.
- Accessibility: Consider ease of access for feeding, cleaning, and collecting eggs. A location near your home or garden can make these tasks more convenient.
Material Selection
- Wood: Wood is a common and readily available material for hen houses. It is relatively inexpensive, easy to work with, and provides good insulation. Consider using treated lumber for longevity and resistance to moisture.
- Metal: Metal, such as galvanized steel or aluminum, offers durability and resistance to pests and weather. However, it can be more expensive than wood and may require additional insulation.
- Plastic: Plastic materials, like recycled plastic lumber, offer low maintenance and resistance to rot and insects. However, they may not provide the same level of insulation as wood or metal.
Types of Hen House Designs
There are numerous hen house designs available, each offering different features and benefits.
Basic A-Frame Design
The basic A-frame design is a simple and popular option for beginner coop builders. It features a sloped roof, typically with a nesting box located at the base of the slope. This design is easy to construct and offers ample space for hens.
Walk-in Coop Design
Walk-in coops provide easy access for cleaning and managing your hens. They feature a larger footprint, allowing you to enter the coop comfortably. This design is ideal for larger flocks or those who prefer a more spacious environment.
Mobile Coop Design
Mobile coops offer flexibility and portability, allowing you to move your hens to different areas of your property. They are typically smaller in size and mounted on wheels or skids. This design is useful for providing fresh grazing areas for your hens and preventing overgrazing in one spot.
Multi-Level Coop Design
Multi-level coops maximize space by incorporating multiple levels for nesting, roosting, and foraging. These designs can accommodate larger flocks and offer a more complex and engaging environment for your hens.
Construction Steps
Constructing a hen house involves several steps, starting with building the frame and then progressing to the walls, roof, and floor. Finally, you will install essential features like nesting boxes, roosting bars, and feeders.
Frame Construction
The frame provides the structural foundation for your hen house. It is typically made of treated lumber, which is resistant to moisture and decay.
- Cut the lumber: Begin by cutting the lumber to the desired dimensions for the frame. You will need to cut pieces for the base, walls, and roof.
- Assemble the base: Use screws or nails to connect the base pieces, creating a rectangle or square. Ensure that the base is level and stable.
- Erect the walls: Attach the wall pieces to the base using screws or nails. Ensure the walls are plumb (vertical) and square.
- Construct the roof: Cut the roof pieces and attach them to the top of the walls. You can use a simple gable roof design for a traditional look.
- Secure the frame: Once the frame is complete, reinforce it by adding diagonal bracing for extra support. This will prevent the frame from warping or sagging over time.
Wall Construction
The walls of your hen house should be insulated and weatherproof to protect your chickens from the elements.
- Install the sheathing: After the frame is assembled, attach sheathing to the walls. This can be plywood, OSB (oriented strand board), or other suitable material. Sheathing provides a solid surface for the exterior cladding.
- Add insulation: If you live in a cold climate, consider adding insulation to the walls. This will help keep the hen house warm during winter. You can use fiberglass batts, foam board, or other insulation materials.
- Install the exterior cladding: The exterior cladding should be weatherproof and durable. Options include wood siding, metal siding, or vinyl siding.
Roof Construction
The roof protects your chickens from rain, snow, and sun.
- Install roofing felt: Before adding shingles, apply roofing felt to the roof. This will create a water-resistant barrier.
- Install shingles: Choose a roofing material that is durable and weatherproof. Options include asphalt shingles, metal shingles, or tile shingles.
- Add a vent: Ensure adequate ventilation in the hen house by installing a vent in the roof. This will help regulate temperature and humidity.
Floor Construction
The floor should be durable and easy to clean.
- Install a subfloor: Attach a subfloor to the frame. This can be plywood, OSB, or other suitable material.
- Add a layer of bedding: Cover the subfloor with a layer of bedding material. Options include straw, wood shavings, or pine shavings.
Installing Essential Features
Once the structure is complete, install nesting boxes, roosting bars, and feeders.
- Install nesting boxes: Nesting boxes provide a private and comfortable space for your hens to lay eggs. Place them in a quiet corner of the hen house.
- Install roosting bars: Roosting bars are essential for chickens to sleep and rest. Position them at a height that is comfortable for your chickens.
- Install feeders and waterers: Provide easy access to food and water by installing feeders and waterers in the hen house.
Security and Safety
Your hens are vulnerable to various predators, from small rodents to larger animals like raccoons, foxes, and even hawks. Protecting them from these threats is crucial for their well-being and the success of your flock.
Securing the Hen House
A secure hen house is the first line of defense against predators.
- Solid Construction: Use sturdy materials like plywood, metal, or concrete for the walls and roof. Avoid using thin or flimsy materials that can be easily breached.
- Secure Doors and Windows: Ensure all doors and windows are tightly sealed and have secure latches or locks. Consider using metal hinges and reinforced door frames.
- Predator-Proof Fencing: Surround the hen house with a strong, predator-proof fence that extends at least 2 feet underground to prevent burrowing animals from entering. Use a fine mesh wire that prevents small predators from squeezing through.
- Elevated Housing: If possible, consider raising the hen house off the ground to make it more difficult for ground predators to reach.
- Lighting: Install adequate lighting around the hen house to deter nocturnal predators. Motion-activated lights can also be effective in startling potential intruders.
Ensuring Hen Safety Within the Hen House
Once the hen house is secure, focus on creating a safe environment for your hens inside.
- Predator-Proof Roosting Areas: Provide roosting bars that are high enough to prevent predators from easily reaching the hens.
- Nest Boxes: Ensure nest boxes are securely attached and have a small entrance that is difficult for predators to access.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is essential for the health and safety of your hens. Ensure the hen house is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of ammonia and other harmful gases.
- Cleanliness: Regularly clean the hen house to remove droppings and other debris. This helps to prevent the spread of diseases and parasites.
- Predator Deterrents: Consider using predator deterrents such as predator urine or ultrasonic devices to discourage predators from approaching the hen house.
Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance of your hen house is crucial to ensure the health and well-being of your chickens and to extend the lifespan of your structure. By following a simple maintenance schedule, you can prevent disease outbreaks, keep your chickens comfortable, and enjoy fresh eggs for years to come.
Cleaning and Disinfecting
Cleaning and disinfecting your hen house is a crucial part of maintaining a healthy environment for your chickens. It helps to prevent the spread of diseases and parasites.
- Regular Cleaning: Daily cleaning of the hen house is essential. Remove droppings, spilled feed, and any other debris. This will help to reduce the build-up of ammonia, which can be harmful to your chickens.
- Weekly Deep Cleaning: At least once a week, you should thoroughly clean the entire hen house. This includes removing all bedding, cleaning the nesting boxes, and scrubbing the floor and walls. Use a mild detergent and water to clean the hen house, followed by a rinse with clean water.
- Disinfecting: After cleaning, disinfect the hen house using a poultry-safe disinfectant. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Common disinfectants include bleach diluted in water, vinegar, and iodine solutions.
Tips for Keeping the Hen House in Good Condition
Maintaining a clean and well-maintained hen house is crucial for the health and well-being of your chickens.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining a healthy environment for your chickens. Ensure your hen house has adequate ventilation to allow for fresh air circulation and to prevent the build-up of moisture and ammonia.
- Bedding: Provide a thick layer of bedding for your chickens. This will help to absorb moisture and provide insulation. Common bedding materials include wood shavings, straw, and shredded paper.
- Nesting Boxes: Provide a sufficient number of nesting boxes for your chickens. Ensure the nesting boxes are clean and comfortable.
- Perches: Perches are essential for your chickens to roost at night. Ensure the perches are the right height and diameter for your chickens. They should be placed at a comfortable height and should not be too close to the walls or floor.
- Water and Feeders: Provide clean water and fresh feed daily. Ensure the waterers and feeders are clean and accessible to your chickens. Regularly check the waterers and feeders for cleanliness and to ensure there is no blockage.
Budgeting and Cost Estimation
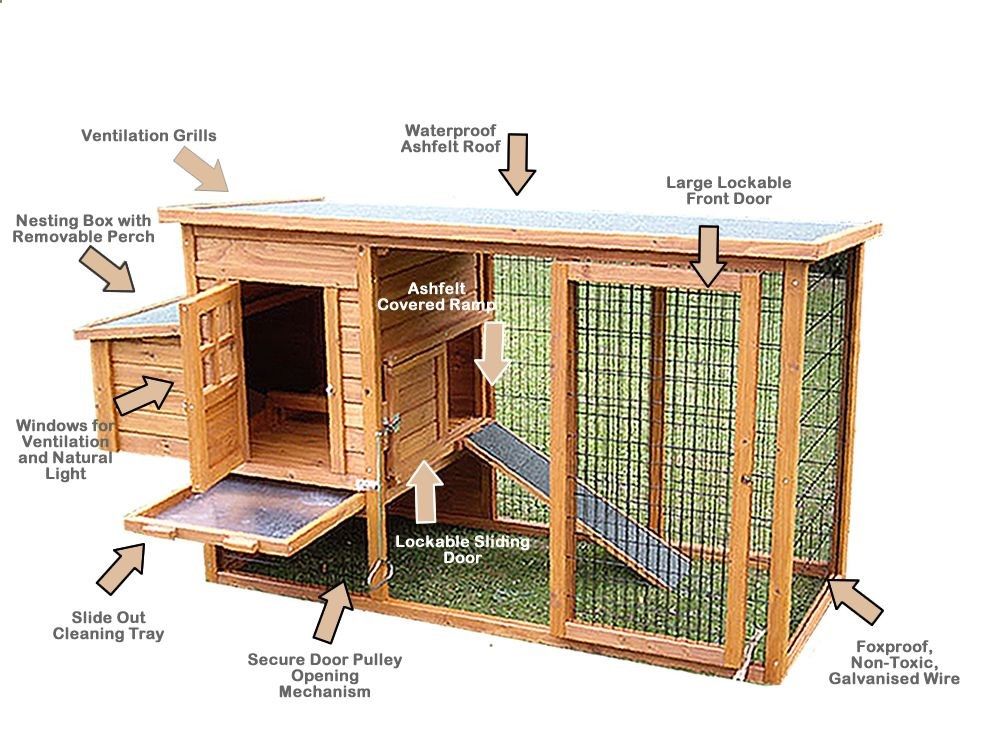
Building a hen house can be a fun and rewarding project, but it’s important to factor in the cost before you start. The price can vary depending on the size, materials, and features you choose.
Here’s a breakdown of the factors that influence the cost of building a hen house:
Size and Design
The size of your hen house will be a major factor in determining the cost. A larger hen house will require more materials, labor, and possibly even specialized construction techniques. The design also plays a role. A simple, rectangular coop will be less expensive than a more elaborate, multi-level structure.
Materials
The type of materials you choose will significantly affect the cost. Wood is a common and affordable material, but you can also use other options like metal, concrete, or recycled materials. The quality of the materials will also impact the price. For example, pressure-treated lumber is more expensive than regular lumber but is more resistant to rot and decay.
Features
The features you include in your hen house will also add to the cost. These can include things like nesting boxes, roosting bars, windows, doors, and ventilation systems.
Labor
If you’re doing the construction yourself, you’ll only need to factor in the cost of materials. However, if you’re hiring a contractor, you’ll need to budget for their labor costs.
Sample Budget Breakdown
Here’s a sample budget breakdown for a small, basic hen house that can accommodate 4-6 hens:
| Item | Quantity | Cost per Unit | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lumber | 100 board feet | $5.00/board foot | $500.00 |
| Hardware | (screws, nails, hinges, etc.) | $50.00 | $50.00 |
| Roofing Materials | (shingles, underlayment, etc.) | $100.00 | $100.00 |
| Nesting Boxes | 2 | $20.00/box | $40.00 |
| Roosting Bars | 1 | $10.00 | $10.00 |
| Door | 1 | $50.00 | $50.00 |
| Window | 1 | $25.00 | $25.00 |
| Paint | 1 gallon | $30.00 | $30.00 |
| Total | $805.00 |
This is just a sample budget, and your actual costs may vary depending on the factors mentioned above.
Tips for Saving Money
Here are some tips for saving money on materials and construction:
- Shop around for the best prices. Compare prices from different lumberyards, hardware stores, and online retailers. You can often find significant savings by doing your research.
- Consider using recycled materials. You can often find free or inexpensive materials like pallets, old doors, and windows. These can be repurposed to create unique and budget-friendly hen houses.
- Do the construction yourself. If you have the skills and time, doing the construction yourself can save you a lot of money on labor costs.
- Build a smaller hen house. A smaller hen house will require fewer materials and can be a more affordable option.
- Keep it simple. Avoid adding unnecessary features or embellishments. Focus on the essentials and you can save money without sacrificing functionality.
Final Review
Building a DIY hen house is a fulfilling project that combines practicality with creativity. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can construct a durable and attractive hen house that provides your chickens with a comfortable and secure home. With a little planning, effort, and a touch of personal style, you can create a chicken haven that will be the envy of your neighborhood.
Building a DIY hen house can be a rewarding project, and it’s a great way to ensure your chickens have a safe and comfortable home. If you’re looking for inspiration for your hen house design, consider incorporating a raised garden bed, like the ones featured on this website , to create a self-sustaining ecosystem.
A raised garden bed can provide fresh herbs and vegetables for your chickens, and the compost from their coop can be used to fertilize the garden.